CYTOREDUCTIVE SURGERY + HIPEC (CRS + HIPEC)
What is the peritoneum/peritoneal surface?
The peritoneum is the inner lining of the abdomen which also lines the inner organs of the abdomen. It secretes fluid which decreases friction between the organs and insulates the organs.
Need for peritoneal surface malignancy unit? Why need one?
The advanced cancers inside the abdominal cavity are the most difficult cancers to treat and hence need an experienced and expert team of doctors to manage. These patients if properly diagnosed and treated with the best available treatments can be offered a chance at a cure.
Dr. SUHAS K R at Narayana multispecialty hospital started this program with the intention to give patients belonging to Mysore and surrounding districts the chance to get the best of treatment at a reasonable cost as it is difficult for many of the patients to go to metro cities. Since starting the program, we have treated around 30 patients with excellent results which is the highest in Mysuru and one of the highest in the whole of Karnataka. This is the first of its kind unit in the Mysuru region and there is a need for patient awareness about such a program so that they can avail the benefits.
Which advanced cancers can be treated in this unit?
- Ovarian cancer
- Large and small bowel cancer
- Appendiceal cancer
- Primary peritoneal cancer
- Stomach cancer
Which are the patients?
- Patients who have swelling in the abdomen
- Abdomen filled with fluid (ascites)
- Cancer which has spread inside the abdomen
Why specialist care?
Advanced cancer needs specialist management to have the best chance at a cure. Surgery needs to be thorough and ensure 100% removal of cancer and without adequate surgery, nothing else will ensure the best chance at a cure for the patient.
What are the special treatment options for the patients?
Cytoreductive surgery – this means the removal of the entire peritoneum which is the inner lining of the abdomen along with the removal of all cancer-affected organs inside the abdomen. This is a complicated procedure usually lasting more than 8-10 hours as the cancer surgeon has to ensure 100% removal of visible cancer. The surgery includes (animated video in the videos section)
- Greater omentectomy
- Bilateral upper quadrant peritonectomy
- Bilateral paracolic quadrant peritonectomy
- Pelvic peritonectomy with or without anterior resection of recto-sigmoid colon
- Lesser omentectomy
- Total hysterectomy with bilateral scalping oophorectomy.
- Bilateral pelvic node clearance.
- Appendicectomy
- Cholecystectomy
- Right or total colectomy
- Splenectomy
- Partial or total gastrectomy
In simple terms, all the affected organs inside the abdomen have to be removed to ensure a chance at a cure.
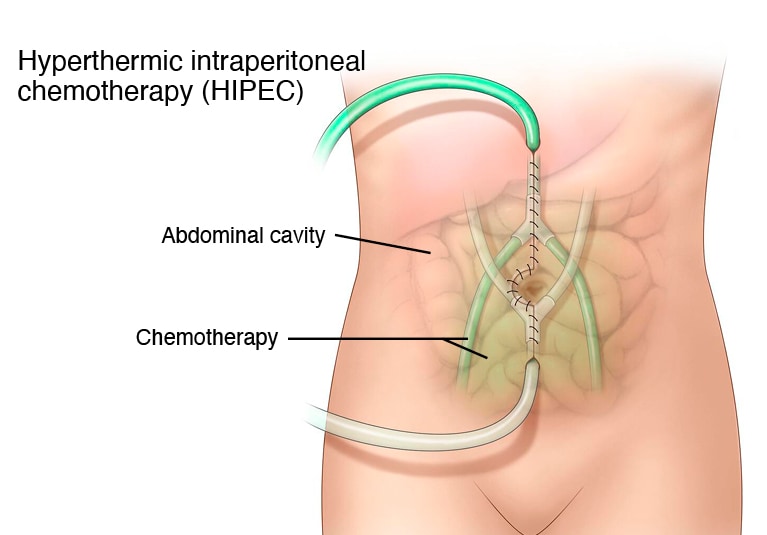
HIPEC – hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy - this means the chemotherapy drug is heated to 41 c and circulated inside the abdomen after the surgery for a period of 90 minutes. The higher temperature achieved inside the abdomen increases the effect of the drug on cancer cells as well as heat itself causes deleterious effects on cancer cells. Intraperitoneal chemotherapy decreases the body's exposure to chemotherapy as well as achieves a high concentration of drug inside the abdomen to ensure the best results.
For the majority of the patients in whom cancer has spread to the peritoneum the procedure is done is a combination of cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC which has shown better results than just giving chemotherapy or surgery(Animated video in the video section).
PIPAC - Pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy – chemotherapy drug is given inside the abdomen through keyhole surgery as aerosols. This method of the direct delivery of drugs in small doses than usual has a good response with minimal side effects of traditional chemotherapy. This is usually given in patients who have fluid inside the abdomen which doesn’t respond to any treatment and in patients who are not considered for surgery upfront.
Intra peritoneal chemotherapy - after surgery chemotherapy is delivered inside the abdomen through a specialized device called a chemo port which decreases the general side effects of chemotherapy drugs but same curative effect.
Specialized chemotherapy and targeted therapies – with the advent of new therapies for cancer patients there are specific drugs available for specific gene mutations eg BRCA gene. Each patient is assessed for eligibility for these targeted drugs which offer lesser toxicity than traditional chemotherapy.
Chemo port insertion - a specialized device that obliviates the need for repeated pricking in the arms for blood samples or chemotherapy.
Genetic counseling - Some cancers are hereditary (run in families) and are transmitted through defective genes. We have targeted therapies available for some of these mutations which help us in curing these patients.
Cancer prevention –
- Dietary counseling
- Counseling for people with addictions like tobacco and alcohol
- Surgeries to prevent cancer- in patients with a high risk of cancer
- Prophylactic removal of ovaries and/or breast in patients with BRCA
- Prophylactic removal of large bowel/colon.
Screening - for people with a low and high risk of cancer. In patients with a high risk of cancer the screening needs to be more frequent than routine and may involve different imaging than normal people.
Complications after this procedure?
In a procedure which is of such a big magnitude complications are expected to happen and that’s why patient selection as well as preparation for surgery is very important. Complications include bleeding, infection, pulmonary complications like pneumonia, and pulmonary embolism, and cardiac complications like infarction can happen and needs to be managed appropriately.
Quality of life after this treatment
One of the most important queries patients have is what happens to patients after undergoing such a long-complicated procedure? are they bedridden? are they dependent on others for the rest of their lives?
The initial recovery post these procedures is slow with patients getting back to normal diet and routine independent ambulation in 1- 2 weeks. After the recovery, the patient can join back to desk work in one-month time and manual workers may need to delay a bit more. The majority of the patients get back to their normal lives in a few months’ time.